Databricks DE Associate Notes
- Auto generate the column when create table
- Auto Loader (Streaming) vs Copy Into
- Control and Data Plane
- Time Travel
- Temporary View
- UDF
- Permission
- Query external files
- Drop database and all its tables
- Create JDBC table
- Copy table
- Managed/External table
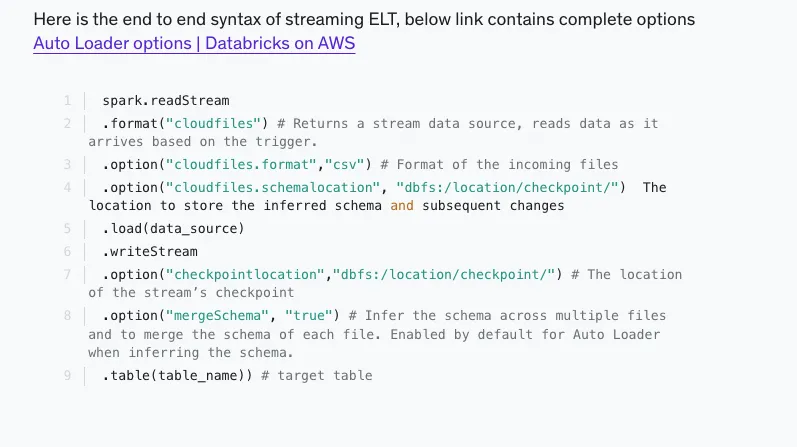
- Structured Streaming
- Delta Live Tables
- Alerts
- Unity catalog
- Running notebook
Auto generate the column when create table
- GENERATED ALWAYS AS (CAST(orderTime as DATE))
Auto Loader (Streaming) vs Copy Into
Identified via cloudFiles in streaming
- Auto loader supports both directory listing and file notification but COPY INTO only supports directory listing.
- Directory listing - List Directory and maintain the state in RocksDB, supports incremental file listing
- File notification - Uses a trigger+queue to store the file notification which can be later used to retrieve the file, unlike Directory listing File notification can scale up to millions of files per day.
- Schema location is used to store schema inferred by AUTO LOADER
- To allow AUTO LOADER to run faster next time
- Use Auto Loader when
- having large number of files
- schema evolve frequently
- COPY INTO keeps track of files that were successfully loaded into the table, the next time when the COPY INTO runs it skips them.
Control and Data Plane
- Control
- Stored in Databricks Cloud Account
- Notebook commands and many other workspace configurations are stored in the control plane and encrypted at rest
- Data
- Stored in Customer Cloud Account
- For most Databricks computation, the compute resources are in your AWS account in what is called the Classic data plane
- Both
- Interactive Notebook
Time Travel
By Timestamp
select * from table TIMESTAMP AS OF "2022-01-01"
By Version Number
select * from table VERSION AS OF 2
select * from table@2
select * from delta.'/path/to/table@2
Restore
RESTORE table TO VERSION as of 2
Temporary View
- Session scoped temp view
- only available with a spark session, so another notebook in the same cluster can not access it
- if a notebook is detached and reattached local temporary view is lost
- Global temp view
- available to all the notebooks in the cluster
- can still be accessed when notebook is detached and attached
- if a cluster restarts global temporary view is lost
UDF
CREATE FUNCTION fn(...)
RETURNS DOUBLE
RETURN <expression>
Permission
GOT: GRANT
To give all permission, use ALL PRIVILEGES
💡 Insert, Update, Delete are combined to
Modify
Usage Privilege
To perform an action on a schema object in the Hive metastore, a user must have the USAGE privilege on that schema in addition to the privilege to perform that action. Any one of the following satisfies the USAGE requirement:
- Be a workspace admin
- Have the
USAGEprivilege on the schema or be in a group that has theUSAGEprivilege on the schema - Have the
USAGEprivilege on theCATALOGor be in a group that has theUSAGEprivilege - Be the owner of the schema or be in a group that owns the schema
Even the owner of an object inside a schema must have the USAGE privilege in order to use it.
Ownership
- Ownership determines whether or not you can grant privileges on derived objects to other users, since Steve is not the owner of the underlying sales table, he can not grant access to the table or data in the table indirectly
- A user who creates the object becomes its owner, does not matter who is the owner of the parent object
Query external files
SELECT * FROM format.`/Location`
format - CSV, JSON, PARQUET, TEXT
CREATE TABLE table_name (col_name1 col_typ1,..)
USING data_source
OPTIONS (key=’value’, key2=vla2)
LOCATION = “/location“
^data_source = CSV, etc
Drop database and all its tables
DROP DATABASE customers CASCADE
Create JDBC table
CREATE TABLE users_jdbc
USING org.apache.spark.sql.jdbc
OPTIONS (
url = "jdbc:sqlite:/sqmple_db",
dbtable = "users"
)
Copy table
Shallow Clone
- Shallow clones just copy the Delta transaction logs, meaning that the data doesn’t move so it can be very quick
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE {new_table_name}
SHALLOW CLONE {source_table_name}|[LOCATION path]
Deep Clone
- It copies all of the data and transaction logs this can take a long time based on the size of the table
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE {new_table_name}
DEEP CLONE {source_table_name}|[LOCATION path]
Managed/External table
Managed
A drop command will drop everything from metastore and storage.
External
A drop command will only drop data but not metadata and logs
Structured Streaming
Limitations
- Multiple streaming aggregations (i.e. a chain of aggregations on a streaming DF) are not yet supported on streaming Datasets.
- Limit and take the first N rows are not supported on streaming Datasets.
- Distinct operations on streaming Datasets are not supported.
- Deduplication operation is not supported after aggregation on a streaming Datasets.
Sorting operations are supported on streaming Datasets only after an aggregation and in Complete Output Mode.
Note: Sorting without aggregation function is not supported.
Properties of structured streaming
- Structured Streaming uses
checkpointingandwrite-ahead logsto record the offset range of data being processed during each trigger interval.
# Once
spark.readStream
.format("delta")
.table("events_log")
.groupBy("customerId")
.count()
.writeStream
.format("delta")
.outputMode("complete")
.option("checkpointLocation", "/tmp/delta/eventsByCustomer/_checkpoints/")
.trigger(once = True)
.table("target_table")
# every 15mins
spark.readStream
.format("delta")
.table("events_log")
.groupBy("customerId")
.count()
.writeStream
.format("delta")
.outputMode("complete")
.option("checkpointLocation", "/tmp/delta/eventsByCustomer/_checkpoints/")
.trigger(processingTime = "15 Minutes")
.table("target_table")
# Available now
spark.readStream
.format("delta")
.table("events_log")
.groupBy("customerId")
.count()
.writeStream
.format("delta")
.outputMode("complete")
.option("checkpointLocation", "/tmp/delta/eventsByCustomer/_checkpoints/")
.trigger(availableNow = True)
.table("target_table")
Output modes
- Append
- Update
- Complete
Active streams
for s in spark.streams.active:
s.stop()
Delta Live Tables
create or replace live table orders_valid
(constraint valid_timestamp expect (timestamp > "2020-01-01") on violation drop row)
select * from live.orders_vw
- DLT pipeline supports two modes Development and Production, you can switch between the two based on the stage of your development and deployment lifecycle.
Development
- Reuses a cluster to avoid the overhead of restarts
- Disables pipeline retries so you can immediately detect and fix errors
Production
- Restarts the cluster for specific recoverable errors, including memory leaks and stale credentials
- Retries execution in the event of specific errors, for example, a failure to start a cluster
DLT Expectations
- CONSTRAINT valid_timestamp EXPECT (timestamp > ‘2020-01-01’)
- Retain
- flag invalid in log
- pipeline continues
- CONSTRAINT valid_timestamp EXPECT (timestamp > ‘2020-01-01’) ON VIOLATION DROP ROW
- Drop
- flag invalid in log
- pipeline continues
- CONSTRAINT valid_timestamp EXPECT (timestamp > ‘2020-01-01’) ON VIOLATION FAIL
- job fail
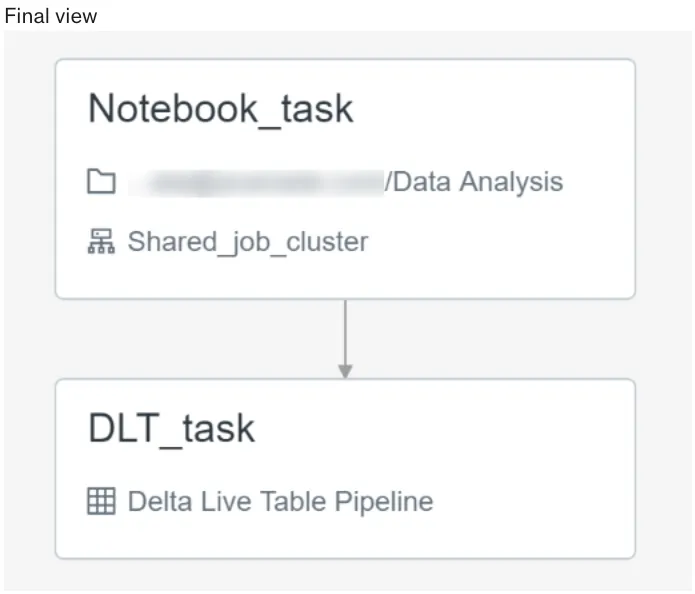
Linking Notebook with DLT
- Single job can be used to set up both notebook and DLT pipeline, use two different tasks with linear dependency
format - CSV, JSON, PARQUET, TEXT
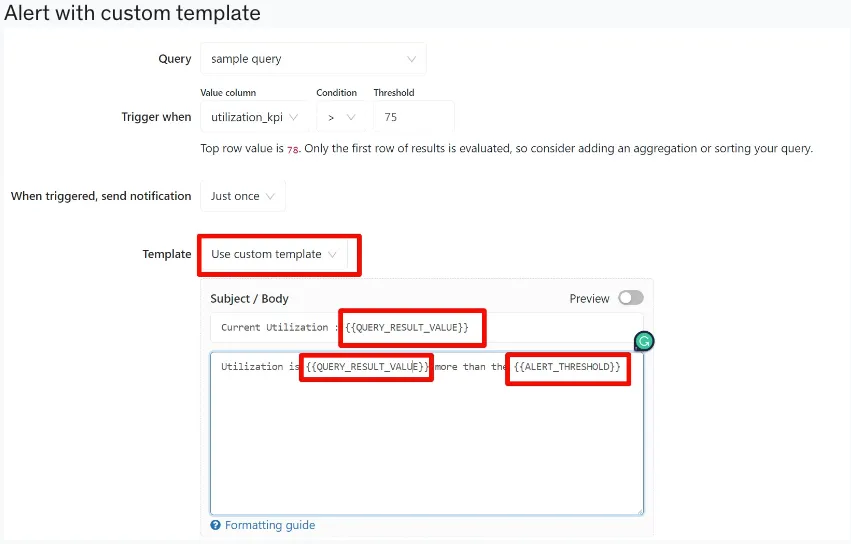
Alerts
- Alerts support custom template supports using variables to customize the default message
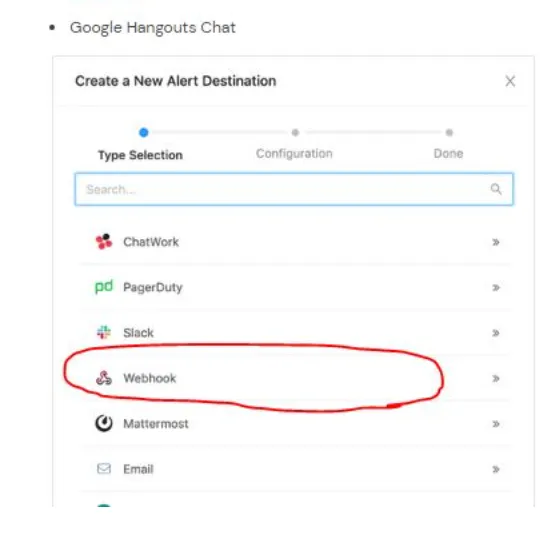
- Alerts support webhook
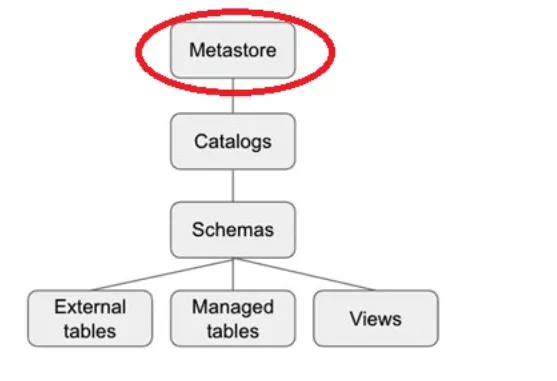
Unity catalog
Running notebook
dbutils.notebook.run(" full notebook path ")
run(path: String, timeout_seconds: int, arguments: Map): String
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: