Airflow Tutorial
Airflow CLI
airflow -h
DAGs
-
airflow list_dags- List all dags
-
airflow dag_state- Get status of dag run
-
airflow test- test task instance without checking dependencies or recording state in db
-
airflow dags trigger <EXAMPLE_DAG>- Trigger the dag
with the current date as execution date
- Trigger the dag
-
airflow dags trigger <EXAMPLE_DAG> -e 2021-01-01- Trigger the dag
with a date in the past as execution date (This won’t trigger the tasks of that dag unless you set the option catchup=True in the DAG definition)
- Trigger the dag
-
airflow dags list-runs -d <EXAMPLE_DAG>- Display the history of
dag runs
- Display the history of
-
airflow dags backfill -s 2024-01-01 -e 2024-01-05 —reset-dagruns <EXAMPLE_DAG>- Backfill from start date to end date
- —reset-dagruns will allow the airflow to run a dag even though it was ran before
- Useful for backfilling jobs where you have made mistake previously
Tasks
-
airflow task_state- Get status of task instance
-
airflow tasks list <EXAMPLE_DAG>- List the tasks contained into the
dag
- List the tasks contained into the
-
airflow tasks test <EXAMPLE_DAG> <EXAMPLE_TASK_IN_DAG> 2021-01-01- Allow to test a task (print_the_context) from a given dag without taking care of dependencies and past runs. Useful for debugging.
Operators
Sensors
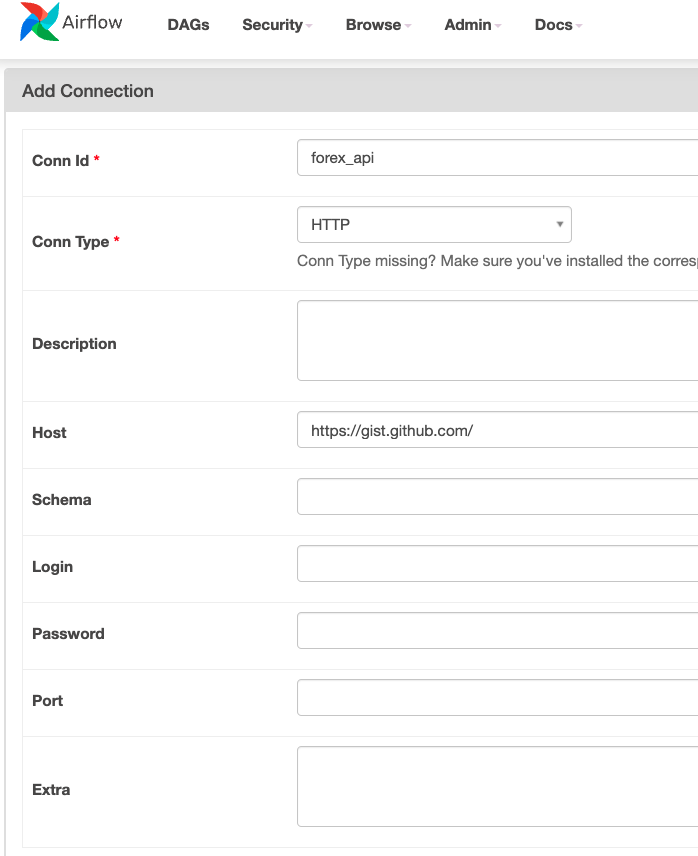
HTTPSensor
# Full endpoint: https://gist.github.com/marclamberti/f45f872dea4dfd3eaa015a4a1af4b39b
is_forex_rates_available = HttpSensor(
task_id="is_forex_rates_available",
http_conn_id="forex_api",
endpoint="marclamberti/f45f872dea4dfd3eaa015a4a1af4b39b",
response_check=lambda response: "rates" in response.text,
poke_interval=5,
timeout=20
)
In AirflowUI Admin → Connection
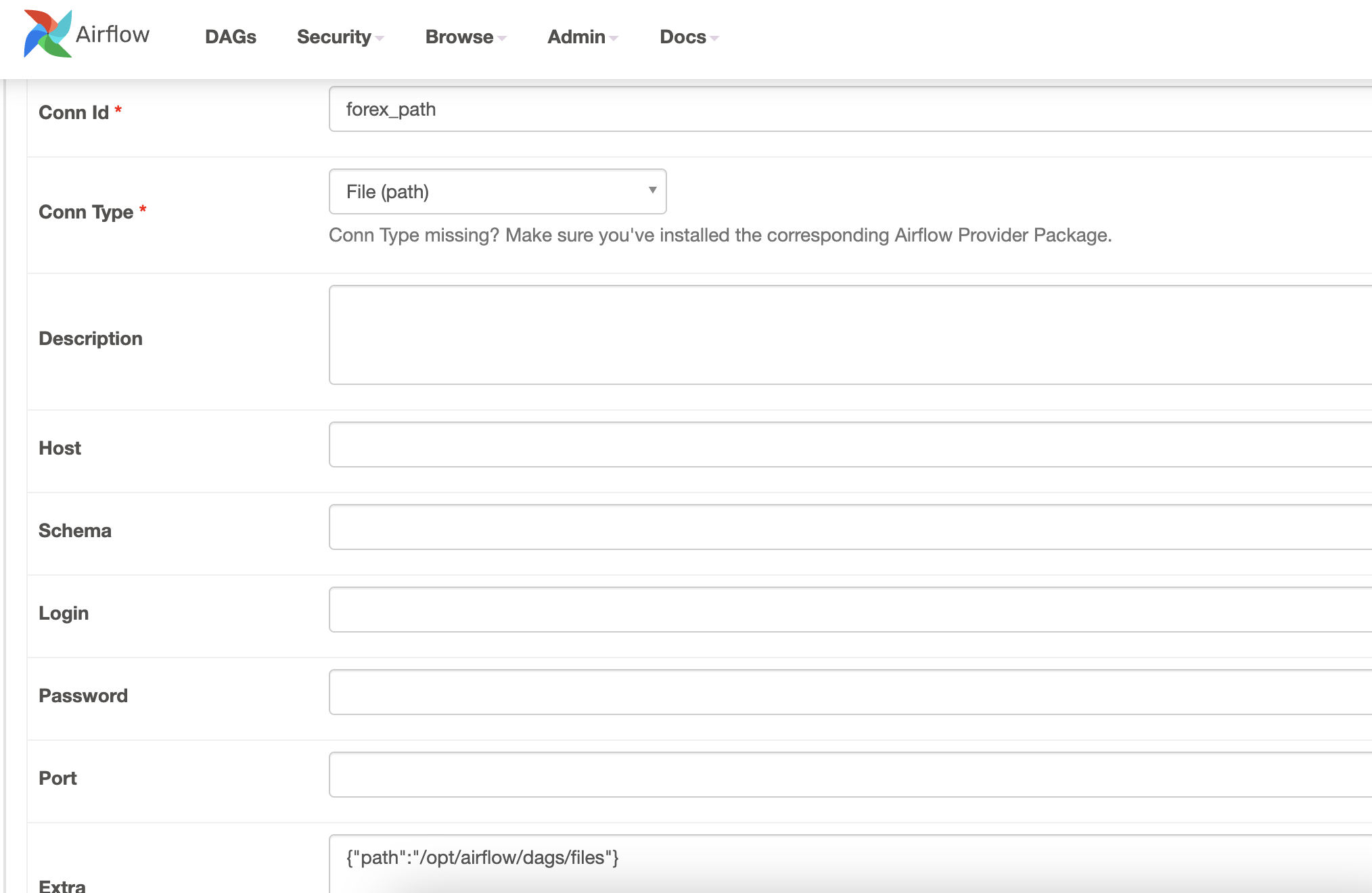
FileSensor
if_forex_currencies_file_avaiable = FileSensor(
task_id="if_forex_currencies_file_avaiable",
fs_conn_id="forex_path", # Base path from forex_path id
filepath="forex_currencies.csv", # Name of file
poke_interval=5,
timeout=20
)
Python Operator
downloading_rates = PythonOperator(
task_id="downloading_rates",
python_callable=download_rates
)
- the python_callable
download_ratesis a python function to be called
Bash Operator
load_forex_rates_to_hdfs = BashOperator(
task_id="load_forex_rates_to_hdfs",
bash_command="""
hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /forex && \
hdfs dfs -put -f $AIRFLOW_HOME/dags/files/forex_rates.json /forex
"""
)
- Need to create a connection on the airflow UI
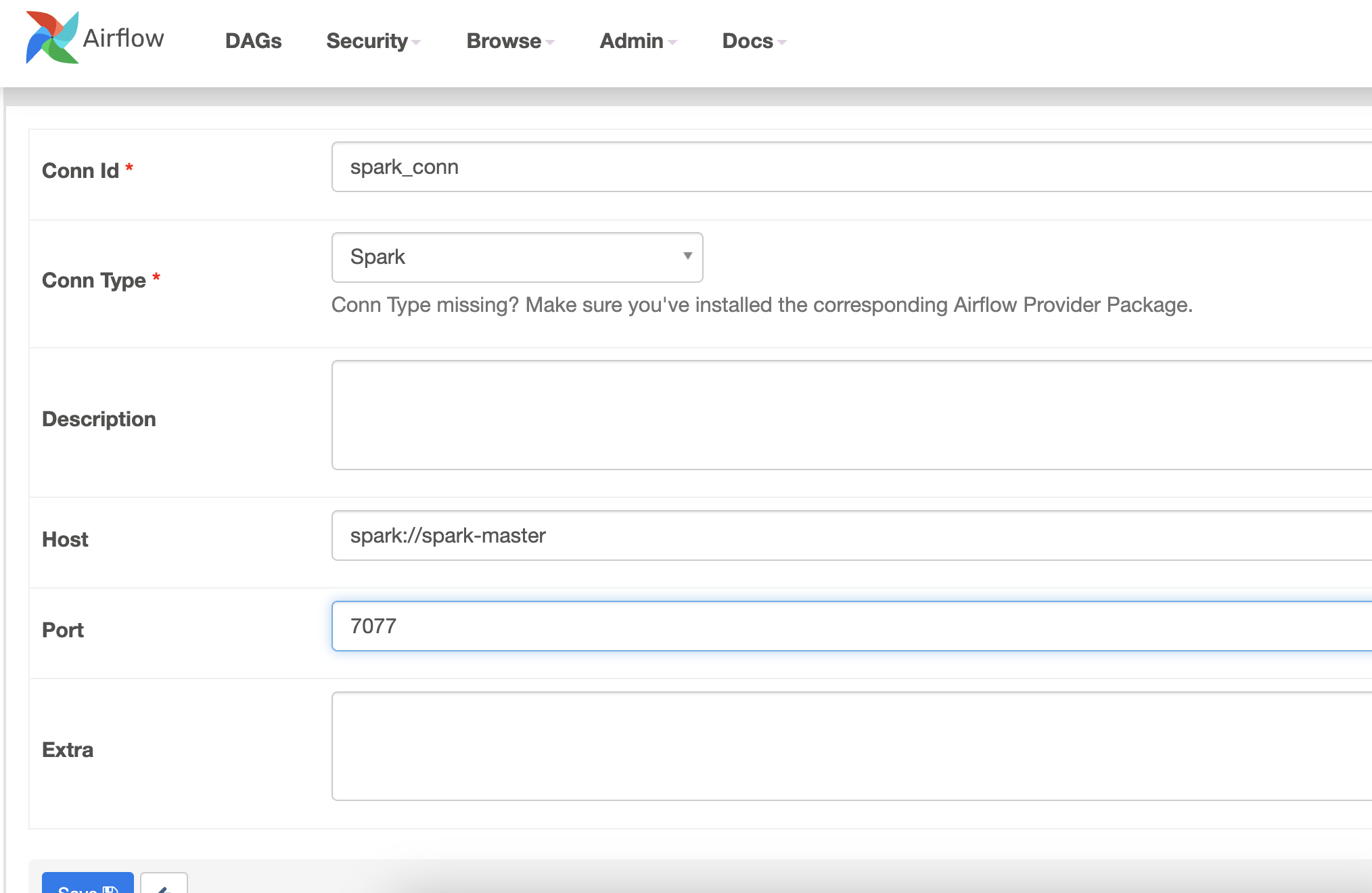
Spark Operator
forex_processing = SparkSubmitOperator(
task_id="forex_processing",
application="/opt/airflow/dags/scripts/forex_processing.py", # Path of the spark script
conn_id="spark_conn",
verbose=False
)
Parameters
Important Params
- start_date - Date which tasks of DAG can be scheduled and triggered
-
datetime.datetime(2019,1,1)- Do not use dynamic values like
datetime.now()
- Do not use dynamic values like
- Set at DAG level through default_args
-
- schedule_interval - Interval of time from min(start_date) at which DAG should be triggered
- Cron (0 * * * *) - preferred
datetime.timedelta(days=1))
💡 A DAG starts being scheduled from
start_dateand triggered after everyschedule_interval
- execution_date - beginning of the processed period
- Given
start_date=2019-09-19T02:00:00 UTCandschedule_interval=every hour- execution_date=2019-09-19T
01:00:00 UTC
- execution_date=2019-09-19T
- Given
- end_date - Date the DAG will stop running
Backfill & Catchup
Backfill
airflow backfill -s 2019-01-20 -e 2019-01-25 --rerun_failed_tasks -B <DAG_ID>
- -s: start date
- -e: end date
- -B: backfill from latest to earliest
Timezones
- Naive - datetime object without the tzinfo
- Aware - datetime object with tzinfo
💡 Always use Aware. Note: datetime obj without timezone IS NOT UTC
local_tz = pendulum.timezone("Europe/Paris")
default_args = {
'start_date': datetime(2019, 3, 29, 1, tzinfo=local_tz),
'owner': 'Airflow'
}
Makes DAG Task Dependent
-
depends_on_past- Set task to depend on previous run - Only run if its the same task in the previous run is successful (Left to right)

-
wait_for_downstream- Set on task level - Task X will wait for tasksimmediatelydownstream of previous instance of task X (In prev dag run) to finish successfully before running

Here DAG Run 3 sleep task waits for DAGRun 2 templated tast (downstream task of the previous DAG) to complete successfully before running.
SLA/Alerts
def on_success_dag(dict):
print("on_success_dag")
print(dict)
def on_failure_dag(dict):
print("on_failure_dag")
print(dict)
default_args = {
'start_date': datetime(2024, 4, 22),
'owner': 'Airflow',
'retries': 3,
'retry_delay': timedelta(seconds=60),
'emails': ['owner@company.com'],
'email_on_failure': True,
'email_on_retry': False
}
with DAG(dag_id='alert_dag',
schedule_interval="44 6 * * *",
default_args=default_args,
catchup=True,
dagrun_timeout=timedelta(seconds=25),
on_success_callback=on_success_dag,
on_failure_callback=on_failure_dag
) as dag:
SLA
-
dagrun_timeout=timedelta(seconds=25)can be used to stop the dagrun in failure
Success/Failure Callbacks
- Allows you to do something when the dag fail/succeed
- Email on failure: To email if dagrun fails
- Email on retry: To email when a retry happens
Unit Testing DAG
- Dag validation test
- Check if there are cycles
- Check default args
- Dag/pipeline definition test
- Check upstream/downstream tasks
- Check number of tasks
- Unit test
- Check logic
- Integration test
- Need dev/test/acceptance/prod env
- End to end pipeline test
- Check output is correct
- Check full logic
- Need dev/test/acceptance/prod env
Environment
- Dev
- Small mock data
- DAG validation + pipeline test
- Unit test
- Test
- Larger real data
- Integration test
- Acceptance
- Copy of prod
- End to end test
- Prod
- Prod
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: